Taurus Constellation: Location, Myth, Picture

Content:
Since ancient times people were observing a beautiful starry sky. They had the custom to combine stars into constellations, naming them by different mythical creatures simultaneously composting myths and legends about them. We wrote an article about the Leo constellation, and today the topic of our article will be another interesting constellation – the Taurus constellation.
Mythology
The mythology of Taurus dates back to ancient Greece. There are two versions of who this Taurus is. According to the first version, Taurus is the supreme god Zeus himself, who has turned into a bull. In Greek mythology, Zeus had a big taste for beautiful women, and now he once again fell in love with the beautiful daughter of the Phoenician king named Europe. Zeus turned into a beautiful white bull and mixed with other bulls in the royal herd. A beautiful bull attracted the attention of a girl who wanted to ride it. Yet as soon as she climbed on the bull, it miraculously transported beautiful Europe on its back to the island of Crete.
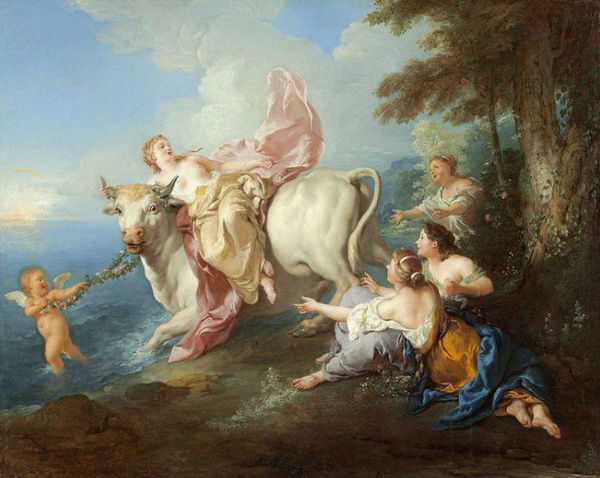

The abduction of Europe by Zeus.
According to the second version, Taurus is a Cretan bull (possibly even the same one that Zeus turned into, and possibly another), defeated by the legendary hero Hercules in his seventh feat. In this sense, the Taurus mythology echoes with the mythology of Leo, because the legendary “star Leo”, as well as the “star Taurus”, was defeated by the brave Hercules, performing his 12 feats.

Hercules is fighting a bull.
However, this constellation was identified with a bull not only by the ancient Greeks but also by other nations, for example, the Babylonians, they called it – “Heavenly Bull”. According to the Babylonian legend, the offended goddess Ishtar sent this heavenly bull to kill one man who rejected her love.
Description
Taurus constellation has the biggest number of stars in the galaxy. Besides this Taurus constellation is very bright; an ordinary person can see 216 stars of this constellation without any optical devices. Taurus constellation occupies almost 800 square degrees of the starry sky.
Location in Sky
Taurus Constellation is located between Gemini constellation and Aries constellation, and in the northwest side of the Orion constellation. Besides these constellations Perseus, Charioteer, Ariadne, and Cetus are next to the Taurus. This constellation is very visible in our temperate latitudes; it can be observed almost all year round, except for the second half of spring and early summer.
How to Find?
The easiest way to find Taurus constellation is to first find a brighter and more noticeable Orion constellation, located slightly lower and to the left of the Taurus. It is logical that Taurus constellation will be higher and to the right of the Orion constellation.

What does a Taurus look like? Just look at this picture.
It is also easy to notice the brightest star in Taurus – Aldebaran; it has a slight orange tint. You can take three stars of the Orion belt – if you draw a conditional line through them and continue it to the right, and then Aldebaran will be on its way.
And if you look even more to the right and above Aldebaran, you can easily see the Pleiades star cluster, a very noticeable and beautiful object in the starry sky.
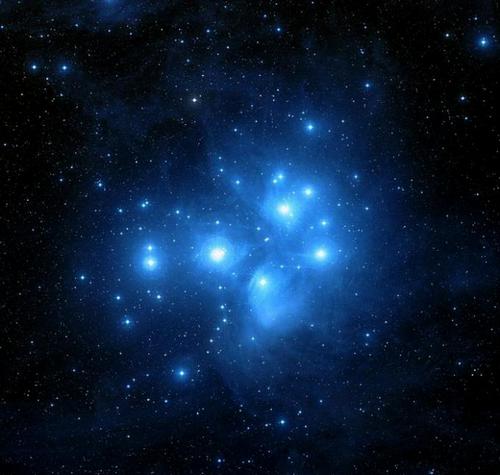

The Pleiades star cluster.
Major Stars
There are a lot of different stars in the Taurus constellation. We will not describe them all, but we will dwell on the largest and brightest ones in more detail.
Aldebaran
Aldebaran is the brightest star in the constellation Taurus, its alpha. The brilliance of Aldebaran is 0.87m. Aldebaran is 13th in the list of the brightest stars of the observed part of the Universe. Aldebaran is an orange giant, a star already quite respectful in age (by stellar standards, of course). At the moment, Aldebaran is burning its helium and is expanding actively; its diameter is 38 times larger than the Sun, although the mass is the same as that of our Sun. At the same time, Aldebaran emits 150 times more light than our star and is only 65 light-years from us. It is practically our close neighbor by galactic standards.
It is also interesting that Aldebaran is a binary star. It has a satellite – a dim red dwarf at a distance of several hundred astronomical units.
If you observe Aldebaran, you may get the impression that it is in the star cluster of Hyades. It has nothing to do with them but simply is in the same direction as Hyades. Only Hyades are located much further from us than our “star neighbor” Aldebaran.

Additional interesting facts about Aldebaran:
- It has the ability to change its brilliance in the most unpredictable way in the range of 0.2m.
- There is a giant planet near Aldebaran, which is 11 times larger than our Jupiter.
Nat
Nat is the second brightest star in the constellation Taurus. Nat is located on the border with the Ascendant constellation, and even for some time belonged to two constellations at once. The star Nat (or El-Nat) is located at a distance 2 times larger than Aldebaran – 131 light-years from us. Nat is 5-6 times larger than our Sun, and 4.5 times heavier.
Nath is a blue giant and, like Aldebaran, is growing. It will become even larger and brighter than Aldebaran over time. Besides this, Nat is also a double star.

Star Nat.
Other Unusual Stars
There are two stars that deserve special attention among the many different stars of Taurus: theta of Taurus – Alcyone and the zeta of Taurus (does not have a separate name).
Alcyone is a bright star in the Pleiades cluster. Alcyone is a multiple star with an unusual structure. There is component A (or Alcyone A) at the center of its system – a Be-type star with an ellipsoid shape and incredibly fast rotation speed (100 times faster than the Sun). In addition, the system contains components B and C – class A0 stars, that is, ordinary stars. There is also component D (Alcyone D) – a white-yellow dwarf. All 4 components of Alcyone can be seen in a small telescope.
Zeta Taurus, located 417 light-years away from us and having a 2.97 magnitude, is notable for the fact that it emits 5,700 times more light than our Sun (!) In other words, it’s some kind of stellar super lantern.
The well-known T Taurus variable deserves special attention. It serves as a prototype for a whole class of variable stars. T Taurus is a very young star that is just forming. Observation of it will help astrophysicists learn more about the origin of stars and the features of their evolution.
Star Clusters and Nebulae
Taurus constellation is famous for its star clusters; first of all, this is a cluster of Hyades and Pleiades. We will dwell on them in more detail.
Hyades Cluster
Hyades are the closest open cluster. Nevertheless, this closest cluster is located at a distance of 153 light-years from us, twice as far as the star of Aldebaran. Messier did not include this cluster in his catalog for the reason that it is quite bright and very scattered. Sometimes Hyades was even considered as a separate constellation.
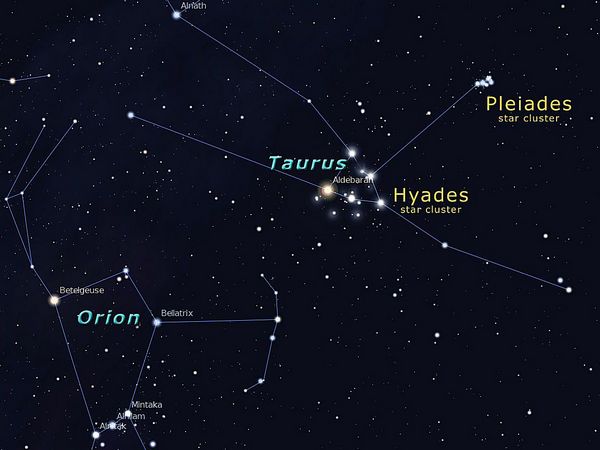
Hyades cluster in the constellation Taurus.
The Hyades cluster is older than the Pleiades and has a diverse stellar composition: some stars are similar in characteristics to our Sun, some are red giants (stars of a more “respectful age”).
It is also worth noting that the Hyades cluster is moving away from us, and it will be difficult to observe it from the Earth after millions of years.
Pleiades Cluster
The Pleiades cluster is the formation of seven bright stars named after the daughters of the mythical king Atlas and his wife Pleiaons: Alcyone, Taiget, Meron, Celen, Electra, Asteron and Maya (united by the common name, the Pleiades). According to Greek myth, the god Zeus placed them in the sky when Orion attacked the Pleiades. Yet even here Orion (though already in the form of a constellation) does not take eyes off them.
The Pleiades are located to the right of Aldebaran and have the shape of a bucket, making them relatively easy to find in the starry sky even without the help of a telescope.
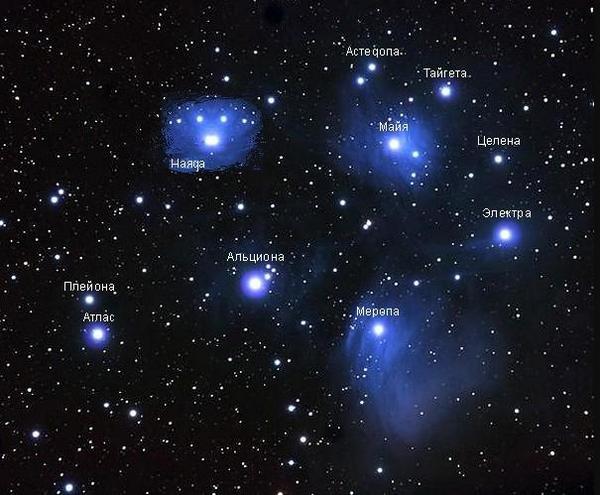

The main stars of the Pleiades cluster.
All the main stars of this cluster are hot white giants with powerful luminosity, but besides them, there are hundreds of other stars that are not so bright. There are stars like our Sun, and white giants among them. By the way, stars the size of the Sun in the Pleiades cluster are visible only through a telescope. Yet there are no red giants here, since, as we know, red giants are precisely the stars of “old” age, “teenage stars” prevails right there.
The Pleiades cluster is very young by galactic standards, its “only” 100 million years old. It is also interesting that there are nebulae near the stars of Meropa and Maya. Before scientists believed that they were the remains of the gases from which the stars themselves were formed, but now the prevailing view is that the nebulae have nothing to do with the Pleiades cluster stars, but simply got caught on their way.
Crab Nebula
The crab Nebula is the most curious and remarkable object that is part of Taurus. The Crab Nebula became the first object listed in the Messier catalog. The Crab Nebula arose as a result of a powerful supernova explosion that was even observed on Earth back in 1054 (medieval Arab and Chinese astronomers wrote about this event). Of course, this explosion did not occur in 1054, but 6500 years before, the light from it reached the Earth just in 1054.
The Crab Nebula is the remnants of a supergiant that has dropped its substance due to the collapse and explosion that followed. It represents a giant cloud that stretches for 11 light-years, and moreover, this cloud continues to expand at a speed of 1,500 km per second.
Astronomers discovered a pulsar – a neutron star with a diameter of only about 30 km with a mass 2.5 times larger than the Sun in the center of the Crab Nebula in 1968. This pulsar rotates at a speed of 30 revolutions per second. Observing it gives a lot of valuable information to astronomers.

Crab Nebula.
You can see it only with night vision binoculars or through a telescope. . Interestingly, due to the high rate of expansion, its shape has been changing for decades.
References and Further Reading
- Allen, Richard Hinckley. Star names: their lore and meaning. — corrected. — Dover Publications, 1963. — С. 383. — ISBN 978-0-486-21079-7.
- Chartrand, Mark R. Skyguide: A Field Guide for Amateur Astronomers. — Golden Books Publishing Company, 1983. — ISBN 0-307-13667-1.
- Levy, David H. Deep Sky Objects. — Prometheus Books (англ.)русск., 2005. — ISBN 978-1-59102-361-6.
- O’Meara, Stephen James. Deep-sky companions: the secret deep. — Cambridge University Press, 2011. — ISBN 978-0-521-19876-9.
- Ridpath, Ian; Tirion, Wil. Monthly sky guide. — 6th. — Cambridge University Press, 2003. — ISBN 978-0-521-53306-5.

Author: Pavlo Chaika, Editor-in-Chief of the journal Poznavayka
When writing this article, I tried to make it as interesting and useful as possible. I would be grateful for any feedback and constructive criticism in the form of comments to the article. You can also write your wish/question/suggestion to my mail pavelchaika1983@gmail.com or to Facebook.

